Mol Biol Evol: Genomic signature of selective sweeps illuminates adaptation of Medicago truncatula to root-associated microorganisms (2015)
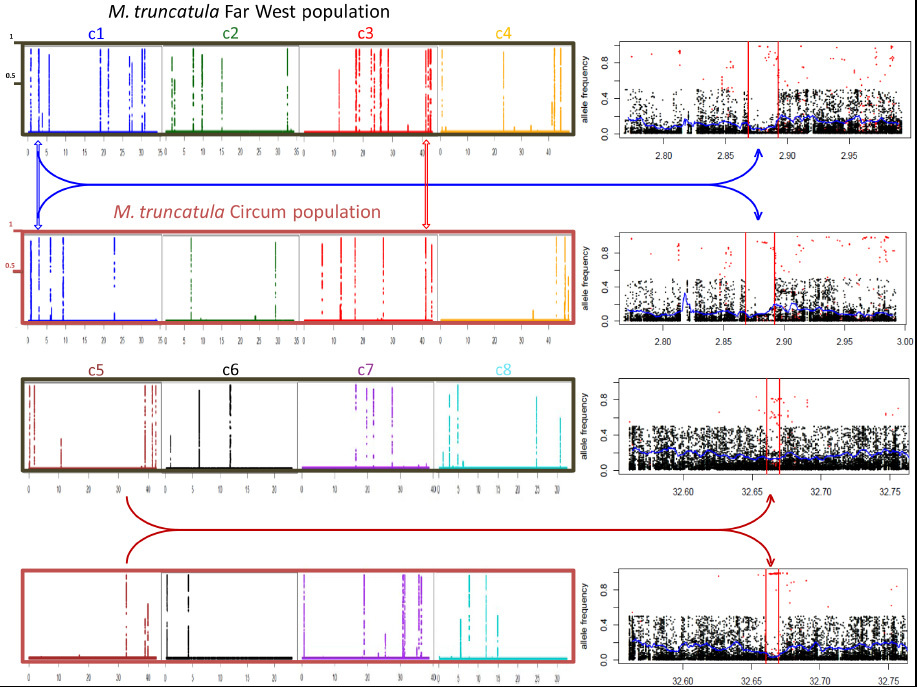
Medicago truncatula is a model legume species used to investigate plant-microorganism interactions, notably root symbioses. Massive population genomic and transcriptomic data now available for this species open the way for a comprehensive investigation of genomic variations associated with adaptation of M. truncatula to its environment. Here we performed a fine-scale genome scan of selective sweep signatures in Medicago truncatula using more than 15 million SNPs identified on 283 accessions from two populations (Circum and Far West), and exploited annotation and published transcriptomic data to identify biological processes associated with molecular adaptation. We identified 58 swept genomic regions with a 15 kb average length and comprising 3.3 gene models on average. The unimodal sweep state probability distribution in these regions enabled us to focus on the best single candidate gene per region. We detected two unambiguous species-wide selective sweeps, one of which appears to underlie morphological adaptation. Population genomic analyses of the remaining 56 sweep signatures indicate that sweeps identified in the Far West population are less population-specific and probably more ancient than those identified in the Circum population. Functional annotation revealed a predominance of immunity-related adaptations in the Circum population. Transcriptomic data from accessions of the Far West population allowed inference of four clusters of co-regulated genes putatively involved in the adaptive control of symbiotic carbon flow and nodule senescence, as well as in other root adaptations upon infection with soil microorganisms. We demonstrate that molecular adaptations in Medicago truncatula were primarily triggered by selective pressures from root-associated micro-organisms.
Source: mbe.oxfordjournals.org
See on Scoop.it – Virology and Bioinformatics from Virology.ca